What are fuses?
Fuses are the protectors, these are the safety devices which are used to protect the home appliances like televisions, refrigerators, computers with damage by high voltage. The fuse is made up of thin strip or strand of metal, whenever the heavy amount of current or an excessive current flow is there in an electrical circuit, the fuse melts and it opens the circuit and disconnects it from the power supply. Also, it works as a circuit breaker or stabilizer which protects the device from damage.In the market, many types, features, and design of fuses are available nowadays. Their strips are made up of aluminum, copper, zinc & it is always connected in series with the circuit to protect from overcurrent in the running cables. Here is the basic circuit diagram & symbol of the fuse.
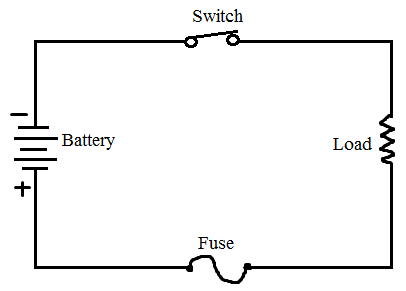

Why do we Need Fuse?
Fuses are used for the prevention of home appliances from the short circuit and damage by overload or high current etc. If we don’t use fuses, electrical faults occur in the wiring and it burns the wire andelectric appliances and may starts fire at home. The lives of television, computers, radios and other home appliances may also put at risk. When the fuse goes, a sudden spark occurs which may lead to turning your home into sudden darkness by disconnecting the power supply which saves any further mishappenings. That’s why we need fuses to protect our home appliances from harm.
How Does Fuse work?
The fuses work on the principle of the heating effect of the current. It’s made up of thin strip or strand of metallic wire with noncombustible material. This is connected between the ends of the terminals. Fuse is always connected in series with the electrical circuit.
When the excessive current or heat is generated due to heavy current flows in the circuit, the fuse melts down due to the low melting point of the element and it opens the circuit. The excessive flow may lead to the breakdown of wire and stops the flow of current. The fuse can be replaced or changed with the new one with suitable ratings. The fuse can be made up of the element like zinc, copper, silver &aluminum. They also act as a circuit breaker which is used to break the circuit when the sudden fault occurs in the circuit. This is not only a protector but it is also used as a safety measure to prevent humans from hazards. So, this is how the fuse operates. Here is the figure is shown fuse operation, fuse barrel(container), fuse link.

How to choose a Fuse?
Fuse rating = (watts/volts) x 1.25
- Select the fuse, like time-delay fuses for inductive load and fast acting fuses for the resistive load.
- Write down the power(watts) of the appliance – usually from the appliance manual,
- Write down the voltage rating. The voltage must be greater than the circuit voltage for the proper protection of the device.
- Use the next highest fuse rating after the calculation. For example, if the calculated fuse rating is 8.659 amps, so for this we will use a 9 amp fuse.
Characteristics of Fuses
There are some of the important characteristics of the fuses in the electrical and electronic system which are as follows:-
- Current Rating: The continuously conducting maximum amount of current holds the fuse without melting it is termed as current ratings. It is the current carrying capacity, which is measured in Amperes. This is the thermal characteristics.
Current(Cin)=75%Current (rating)
- Voltage Rating: In this characteristic, the voltage connected in series with fuse does not increase voltage rating. i.e.,
V(fuse) >V(open ckt)
- I2t Rating: This is the amount of energy which is carried by fuse element whenthere is an electrical fault or some short circuit happens. It measures the heat energy(energy due to current flow) of fuse & it is generated when fuse has blown.
- Interrupting or Breaking Capacity: It is the maximum rating of current without harm interrupt by the fuse is known as breaking or interrupting capacity of the fuse.
Breaking capacity > maximum rated voltage
Breaking capacity <short ckt current
- Voltage Drop: When excessive current flows, the fuse element melts and opens the circuit. Due to this resistance change and the voltage drop will become lesser.
- Temperature: In this, the operating temperature will be higher, therefore the current rating will be lesser, so the fuse melts.

This graph shows the temperature versus the current carrying capacity of the fuse.In this process, at the point where three lines meet at 25 degrees Celsius, the current carrying capacity of the fuse will be 100% and after some time the current capacity decreases at slow blow fuse, it will also decrease up to 82% at 65 degrees C. This results that, increase in temperature will decrease the current carrying capacity of the fuse.
Classification of Fuses
Now we are discussing aboutdifferent types offuses. They are divided into two parts AC Fuses & DC Fuses. Further, they are divided into many categories given in the flowchart below:-
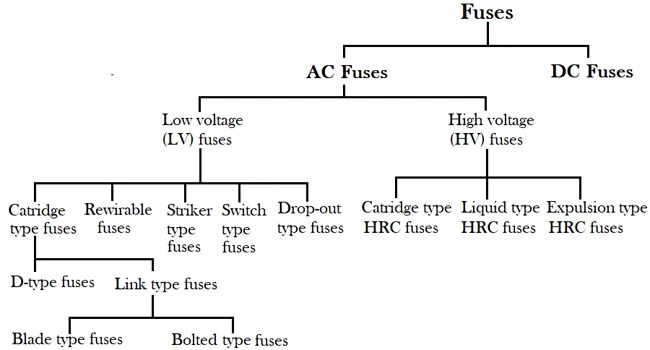
Different Types of Fuses
Fuses are invented first by “Thomas Alva Edison” but nowadays many types of fuses are available in the market. Generally, there are two types of fuses:-
- DC Fuses: DC fuses have larger in size. DC supply has constant value above 0V so it is hard to neglect and turn off the circuit and there is a chance of an electric arc between melted wires. To overcome this, electrodes placed at larger distances and because of this the size of DC fuses get increased.
- AC Fuses: AC fuses are smaller in size. They oscillated 50-60 times in every second from minimum to maximum. So there is no chance of Arc between the melted wires. Hence they can be packed in small size.
AC fuses are further categorized into two parts, i.e., Low voltage fuses and High voltage fuses.
1. Low Voltage Fuses (LV)
- Cartridge Type Fuses: It is the type of fuses in which they have totally closed containers & has the contact i.e., metal besides.

Cartridge Type Fuses are of two types:-
- D-Type Cartridge Fuses:- It is composed of the cartridge, fuse base, cap & adapter ring. The fuse base has the fuse cap, which is fitted with the fuse element with cartridge through adapter ring. The circuit is completed when the tip of the cartridge makes contact with the conductor.
- Link Type Or HRC(High Rupturing Capacity) Fuses:- In this type of fuse, the flow of current by fuse element is given under normal condition. To control the arc which is produced by fuse blown we use the fuse which is made up of porcelain, silver &ceramic. The fuse element container filled with silica sand. The HRC type is again divided into two parts that are:-
- Blade Type/Plug-in Type:- The body of this fuse is made up of plastic and it is easily replaceable in the circuit without any load.
- Bolted Type:- In this type of fuse, the conducting plates are fixed to the fuse base.
- Rewireable/ Kit-Kat Type:- In this type of fuse, the main advantage is that the fuse carrier is easier to remove without having any electrical shock or injury. The fuse base acts as an incoming and outgoing terminal which is made up of porcelain & fuse carrier is used to hold the fuse element which is made up of tin, copper, aluminum, lead, etc. This is used in domestic wiring, small industries etc.

- Striker Type Fuses:- In this type of fuse, it is used for closing and tripping the circuit. They are having enough force and displacement.
- Switch Type Fuses:- In this type of fuse, basically metal enclosed of a switch and a fuse and is far used for low and medium voltage level.
- Drop Out Fuses:- In this type of fuse, the melting of fuse causes the element to drop under gravity about its lower support. They are made for the protection of outdoor transformers.

2. High Voltage Fuses (HV):-
All types of high voltage fuses are used upon the rated voltage up to 1.5 Kv to 138 Kv. High voltage fuses are used to protect the instrument transformers & small transformers. It is made up of silver, copper & tin. When heat generated, the arc produces which causes the boric acid to evolve high amount of gases. That’s why these are used in outdoor places.
These are of three types which are as follows:-
- Cartridge Type HRC Fuses:- It is similar to low voltage type, only some designing features are different.

- Liquid Type HRC Fuses:- These are used for circuit up to 100A rated current& systems up to 132Kv. These fuses have the glass tube filled with carbon tetrachloride. The one end of the tube is packed and another is fixed by phosphorous bronze wire. When fuse operation starts, the liquid uses in the fuse extinguish the arc. This increase the short circuit capacity.
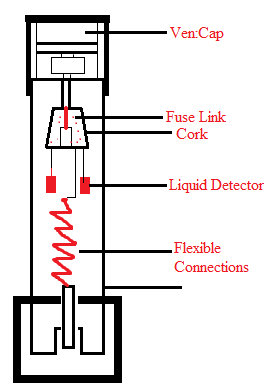
- Expulsion Type HRC Fuses:- It is the escapable fuse, in which expulsion effect of gases produced by internal arcing. In this, the fuse link chamber is filled with boric acid for expulsion of gases.
- Resettable Fuses:- It is the type of fuse, commonly known as self-resetting fuses which uses a thermoplastic conductive type thermistor known as Polymeric Positive Temperature Coefficient (PPTC). If a fault occurs. Current increases, temperature also increase. The increase in resistance is due to increase in temperature. The applications where it is used are military and aerospace where replacement is not possible.

Applications
The fuses are the most important part of electrical and electronics system andcircuits. Here are some applications in which fuses are used, i.e.,
- They are used in home distribution boards, general electrical appliances, and devices.
- They are used in gaming consoles andall automobiles such as car, trucks and other vehicles.
- They are also used in laptops, cell phones, printers, scanners, portable electronics, hard disk drives.
- In the electrical distribution system, you will find fuses in capacitors, transformers, power converters, motor starters, power transformers.
- They are used in LCD monitors, battery packs, etc.